
The man behind organizing the business is called as ‘Organizer’ or ‘Entrepreneur’. The prime aim of it is to a mass wealth in terms of profit. It is normally raised through debt and equity issues. The examples for intangible capital are investment on advertisement, expenses on training programme etc.įinancial Capital means the assets needed by a firm to provide goods and services measured in term of money value. For example, buildings, plants and machinery, factories, inventories of inputs, warehouses, roads, highways etc are tangible capital.
#Factors of production free
Marshall says “capital consists of all kinds of wealth other than free giftsofnature,whichyield income”. Bohm-Bawerk defines it as ‘a produced means of production’. Labour-supply determines its reward (wage).It is both the cause of production and consumer of the product. Labour is less mobile between places and occupations.Labour is inseparable from the Labourer.
#Factors of production manual
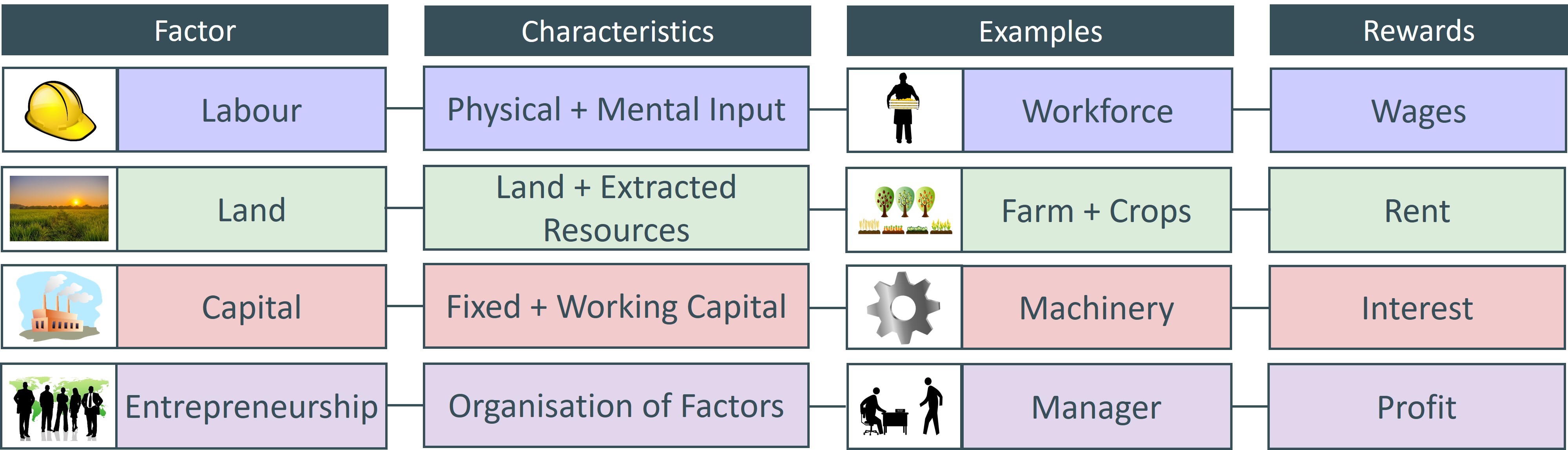
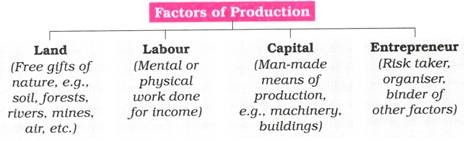
Hence, all aspects of economic life like agriculture, trade and industry are generally influenced by natural resources which are called as “Land” in economics. Industry survives on the availability of coal-mines or waterfall for electricity production. The agricultural products are the basis of trade and industry. The quality and quantity of agricultural wealth are determined by the nature of soil, climate and rainfall. The economic prosperity of a country depends on the richness of her natural resources. Land is the original source of all material wealth. But, in Economics, land means all gifts of Nature owned and controlled by human beings which yield an income. In ordinary sense ‘land’ refers to the soil or the surface of the earth or ground. They have a coordinated impact on production of goods and services. The third and the fourth factors are called ‘secondary factors of production’. Also, organisation or enterprise is a special form of labour. This saved amount is called as capital, which serves as investment in the production process. Thus, saving is production minus consumption. And as consumption of these goods takes place, there is the possibility of some of these goods getting left over. These two factors produce some units of goods for the purpose of consumption. Together, these two factors are called the ‘primary factors of production’. Here, land represents natural resources (such as soil, mineral deposits, seas, rivers, natural forests, fisheries etc). There are of four types viz., land, labour, capital and organization or enterprise. Factors of production means resources used in the process of production of commodities.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
